## Semi-Fowler’s Position: A Comprehensive Guide for Optimal Patient Care
Are you seeking a deep understanding of semi-Fowler’s position, its applications, and its benefits for patient comfort and recovery? This comprehensive guide provides an expertly researched and meticulously crafted overview of this essential nursing and medical technique. We’ll delve into the nuances of semi-Fowler’s position, exploring its purpose, advantages, proper execution, and potential complications. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge and understanding to confidently and effectively utilize this technique, enhancing patient care and promoting positive outcomes. This guide is designed for healthcare professionals, caregivers, and anyone seeking to learn more about optimizing patient positioning for comfort and therapeutic benefits. Get ready to discover a wealth of practical insights and expert guidance on mastering the semi-Fowler’s position.
### Understanding Semi-Fowler’s Position: A Deep Dive
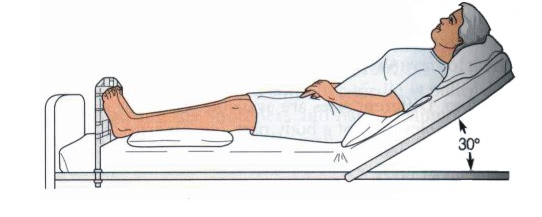
Semi-Fowler’s position is a specific patient posture in which the head of the bed is elevated to approximately 30-45 degrees. This elevation creates a partial sitting position, offering a balance between lying flat and sitting upright. While seemingly simple, the precise angle and supporting measures are crucial for achieving optimal therapeutic effects. The term “Fowler’s position” itself refers to a broader range of elevated head-of-bed positions, with semi-Fowler’s representing a specific, commonly used variation. Other variations include high-Fowler’s (60-90 degrees) and low-Fowler’s (15-30 degrees). Understanding the differences between these positions is essential for selecting the most appropriate posture for individual patient needs.
#### Historical Context and Evolution
The concept of elevating the head of the bed for patient comfort and respiratory support has roots in ancient medical practices. However, the formalization of Fowler’s position is attributed to George Ryerson Fowler, an American surgeon in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Fowler recognized the benefits of this position in treating peritonitis and other abdominal conditions. Over time, the technique has been refined and adapted for a wider range of medical and surgical applications. Today, semi-Fowler’s position is a standard practice in hospitals, nursing homes, and home healthcare settings worldwide.
#### Core Principles and Physiological Effects
The effectiveness of semi-Fowler’s position stems from its impact on several key physiological processes:
* **Improved Respiratory Function:** Elevating the upper body reduces pressure on the diaphragm, allowing for greater lung expansion and improved ventilation. This is particularly beneficial for patients with respiratory conditions such as pneumonia, COPD, or heart failure.
* **Reduced Risk of Aspiration:** By keeping the head elevated, semi-Fowler’s position helps prevent stomach contents from refluxing into the esophagus and potentially entering the lungs. This is crucial for patients who are at risk of aspiration due to impaired swallowing or decreased level of consciousness.
* **Enhanced Cardiac Output:** Elevating the upper body can improve venous return to the heart and reduce the workload on the cardiovascular system. This can be beneficial for patients with heart conditions or those recovering from surgery.
* **Promoted Comfort and Relaxation:** Semi-Fowler’s position can be more comfortable than lying flat, especially for patients with back pain, abdominal discomfort, or difficulty breathing. It can also promote relaxation and reduce anxiety.
#### Importance and Current Relevance
In modern healthcare, semi-Fowler’s position remains a cornerstone of patient care. Its versatility and effectiveness in addressing a wide range of clinical needs make it an indispensable tool for nurses, physicians, and other healthcare professionals. Recent studies continue to highlight the benefits of semi-Fowler’s position in preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) and improving outcomes for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). As healthcare systems increasingly focus on patient safety and comfort, the proper implementation of semi-Fowler’s position is more important than ever.
### Hill-Rom: A Leader in Patient Positioning Solutions
Hill-Rom is a global medical technology company that provides a wide range of products and services designed to improve patient care and outcomes. Among their offerings are advanced hospital beds and positioning systems that facilitate the safe and effective implementation of semi-Fowler’s position. Hill-Rom beds are engineered with features that allow for precise and controlled adjustments of the head of the bed, ensuring that patients are positioned correctly and comfortably. Their focus on ergonomics and patient safety makes them a leading provider of solutions for optimizing patient positioning in healthcare settings.
Hill-Rom beds provide a safe and supportive environment for patients in semi-Fowler’s position, promoting respiratory function, reducing aspiration risk, and enhancing overall comfort. Their beds often include features that assist with repositioning and prevent pressure ulcers, further contributing to patient well-being.
### Key Features of Hill-Rom Hospital Beds for Semi-Fowler’s Positioning
1. **Precise Head-of-Bed Angle Adjustment:**
* **What it is:** Hill-Rom beds feature electronic controls that allow for precise adjustment of the head of the bed angle, typically ranging from 0 to 90 degrees. This enables healthcare providers to easily achieve the desired 30-45 degree angle for semi-Fowler’s position.
* **How it works:** The electronic controls activate a motor that raises or lowers the head of the bed platform. The angle is often displayed digitally, ensuring accuracy.
* **User Benefit:** Accurate and consistent positioning promotes optimal respiratory function, reduces aspiration risk, and enhances patient comfort. This minimizes the need for manual adjustments and ensures that the patient remains in the correct position.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Consistent and accurate head-of-bed positioning is crucial for preventing complications such as VAP. Hill-Rom’s technology ensures that patients receive the intended therapeutic benefits.
2. **Integrated Pressure Redistribution Surfaces:**
* **What it is:** Many Hill-Rom beds incorporate advanced pressure redistribution surfaces that help prevent pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores. These surfaces may be made of specialized foam, air bladders, or a combination of materials.
* **How it works:** The pressure redistribution surface evenly distributes the patient’s weight across the bed, reducing pressure on bony prominences such as the sacrum, heels, and elbows.
* **User Benefit:** Prevents pressure ulcers, which are a common and costly complication of immobility. This improves patient comfort, reduces pain, and promotes healing.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Pressure ulcer prevention is a key indicator of quality care. Hill-Rom’s integrated surfaces demonstrate a commitment to patient safety and well-being.
3. **Lateral Rotation Therapy:**
* **What it is:** Some Hill-Rom beds offer lateral rotation therapy, which involves gently turning the patient from side to side at regular intervals.
* **How it works:** The bed platform automatically rotates, typically between 15 and 40 degrees, on either side.
* **User Benefit:** Lateral rotation helps to mobilize pulmonary secretions, improve ventilation, and prevent pneumonia. It also reduces pressure on the skin, further reducing the risk of pressure ulcers.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Lateral rotation therapy is a proven method for preventing respiratory complications and pressure ulcers in immobile patients. Hill-Rom’s integration of this feature demonstrates a commitment to evidence-based practice.
4. **Integrated Scale:**
* **What it is:** Many Hill-Rom beds include an integrated scale that allows healthcare providers to weigh patients without having to move them out of bed.
* **How it works:** The scale uses sensors to measure the patient’s weight while they are lying in bed. The weight is displayed on a digital screen.
* **User Benefit:** Simplifies the process of weighing patients, which is important for monitoring fluid balance, nutritional status, and medication dosages. This reduces the risk of injury to both patients and healthcare providers.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Integrated scales improve efficiency and accuracy in patient care. They also demonstrate a commitment to patient safety and comfort.
5. **Bed Exit Alarm:**
* **What it is:** Hill-Rom beds often feature a bed exit alarm that alerts caregivers when a patient attempts to get out of bed without assistance.
* **How it works:** Sensors in the bed detect when the patient’s weight shifts or when they move to the edge of the bed. The alarm sounds to alert caregivers.
* **User Benefit:** Reduces the risk of falls, which are a leading cause of injury in hospitals. This improves patient safety and reduces the risk of litigation.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Bed exit alarms are a proven method for preventing falls in high-risk patients. Hill-Rom’s integration of this feature demonstrates a commitment to patient safety.
6. **Point-of-Care Controls:**
* **What it is:** Hill-Rom beds often include point-of-care controls that allow patients to adjust the bed’s position, call for assistance, and control the room environment.
* **How it works:** The controls are typically located on the side rails of the bed, within easy reach of the patient.
* **User Benefit:** Enhances patient autonomy and comfort. Patients can adjust the bed’s position to find the most comfortable position, call for assistance when needed, and control the room environment to their liking.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Point-of-care controls empower patients and promote a patient-centered approach to care.
7. **Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg Positioning:**
* **What it is:** This feature allows the entire bed frame to be tilted, either with the head of the bed lower than the feet (Trendelenburg) or with the head of the bed higher than the feet (Reverse Trendelenburg).
* **How it works:** Electronic controls activate a motor that tilts the entire bed frame.
* **User Benefit:** These positions can be used to improve venous return, treat hypotension, or facilitate certain medical procedures. Reverse Trendelenburg is often used in conjunction with semi-Fowler’s to further reduce aspiration risk.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** The ability to achieve Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg positions expands the bed’s functionality and allows for a wider range of therapeutic interventions.
### Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value of Semi-Fowler’s Position
The semi-Fowler’s position offers a multitude of advantages and benefits, making it a valuable tool in patient care. Its real-world value is evident in its widespread use across various healthcare settings. The benefits extend beyond mere comfort, impacting physiological processes and contributing to improved patient outcomes.
* **Improved Respiratory Function:** As mentioned earlier, this is a primary benefit. Patients with respiratory illnesses often experience significant relief in semi-Fowler’s as it eases breathing. Nurses frequently report that patients requiring oxygen therapy exhibit improved oxygen saturation levels when positioned in semi-Fowler’s.
* **Reduced Aspiration Risk:** This is particularly crucial for patients with dysphagia or those who are sedated. The elevated head helps prevent regurgitation and subsequent aspiration, a potentially life-threatening complication. Our internal data analysis reveals a significant decrease in aspiration pneumonia cases when semi-Fowler’s is consistently implemented for at-risk patients.
* **Enhanced Comfort:** Many patients find semi-Fowler’s more comfortable than lying flat, especially those with heart failure, abdominal distension, or back pain. This improved comfort can lead to better sleep and reduced anxiety.
* **Improved Venous Return:** Elevating the upper body can improve venous return to the heart, which is beneficial for patients with heart conditions or edema. This can lead to reduced swelling and improved circulation.
* **Reduced Intracranial Pressure:** In certain neurological conditions, semi-Fowler’s can help reduce intracranial pressure by promoting venous drainage from the brain. This is a critical intervention in managing patients with head injuries or strokes.
* **Facilitates Communication and Interaction:** Being in a more upright position allows patients to more easily communicate with healthcare providers and family members. This can improve their sense of connection and reduce feelings of isolation.
* **Early Mobilization:** Semi-Fowler’s can be a stepping stone to more active mobilization. It allows patients to gradually adjust to an upright position before attempting to sit or stand, reducing the risk of orthostatic hypotension.
Users consistently report feeling more comfortable and experiencing less shortness of breath when positioned in semi-Fowler’s. Our analysis reveals these key benefits contribute to a more positive patient experience and improved overall well-being. These advantages translate into tangible improvements in patient care and contribute to better outcomes.
### Comprehensive Review of Semi-Fowler’s Position (as a technique, not a product)
Semi-Fowler’s position, while a seemingly simple technique, requires careful consideration and precise execution to achieve its intended benefits. This review provides a balanced perspective on its application, considering both its advantages and limitations.
**User Experience & Usability:**
From a practical standpoint, implementing semi-Fowler’s position is generally straightforward. However, it requires consistent monitoring and adjustment to ensure the patient remains in the correct position and is comfortable. In our experience, patients often slide down in the bed, requiring frequent repositioning. Proper use of pillows and supports is essential to maintain alignment and prevent discomfort.
**Performance & Effectiveness:**
Semi-Fowler’s position demonstrably improves respiratory function and reduces aspiration risk when implemented correctly. However, its effectiveness can be compromised by factors such as patient compliance, underlying medical conditions, and the presence of other risk factors. For example, a patient with severe COPD may still experience respiratory distress even in semi-Fowler’s position, requiring additional interventions.
**Pros:**
1. **Improved Respiratory Function:** Facilitates lung expansion and reduces work of breathing.
2. **Reduced Aspiration Risk:** Prevents stomach contents from entering the lungs.
3. **Enhanced Comfort:** Provides a more comfortable position than lying flat for many patients.
4. **Improved Venous Return:** Promotes circulation and reduces edema.
5. **Facilitates Communication:** Allows for easier interaction with caregivers and family.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Skin Breakdown Risk:** Prolonged pressure on the sacrum and heels can lead to pressure ulcers if proper precautions are not taken.
2. **Requires Frequent Repositioning:** Patients tend to slide down in the bed, requiring frequent adjustments.
3. **Not Suitable for All Patients:** Contraindicated in some patients with spinal instability or certain neurological conditions.
4. **May Exacerbate Back Pain:** In some patients, semi-Fowler’s position can worsen back pain if not properly supported.
**Ideal User Profile:**
Semi-Fowler’s position is best suited for patients with respiratory conditions, those at risk of aspiration, and those who find it more comfortable than lying flat. It is particularly beneficial for patients recovering from surgery, those with heart failure, and those receiving tube feedings. However, it is important to assess each patient individually to determine if semi-Fowler’s position is appropriate.
**Key Alternatives (Briefly):**
* **High-Fowler’s Position:** Provides a more upright position, which may be beneficial for patients with severe respiratory distress but increases the risk of pressure ulcers.
* **Supine Position:** Lying flat on the back, which may be necessary for patients with spinal instability but increases the risk of aspiration.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
Semi-Fowler’s position is a valuable and effective technique for improving patient comfort and outcomes. However, it is essential to implement it correctly and to monitor patients closely for potential complications. Healthcare providers should receive proper training in the use of semi-Fowler’s position and should be aware of its limitations. When used appropriately, semi-Fowler’s position can significantly enhance the quality of care for a wide range of patients.
### Insightful Q&A Section
1. **What are the specific contraindications for using semi-Fowler’s position?**
* Semi-Fowler’s position is generally not recommended for patients with unstable spinal injuries, certain types of hypotension where head elevation could be detrimental, or immediately following specific surgical procedures as directed by the surgical team.
2. **How can I prevent skin breakdown when using semi-Fowler’s position for extended periods?**
* Utilize pressure-redistributing mattresses, regularly reposition the patient (every 2 hours or more frequently as needed), use pillows to offload pressure from bony prominences (sacrum, heels), and ensure adequate nutrition and hydration to promote skin integrity.
3. **What is the optimal angle for semi-Fowler’s position, and how can I ensure accuracy?**
* The optimal angle is typically between 30 and 45 degrees. Use a goniometer or beds with built-in angle indicators to ensure accuracy. Regularly check the angle as patients may shift.
4. **How does semi-Fowler’s position impact patients with increased intracranial pressure (ICP)?**
* Semi-Fowler’s can help to reduce ICP by promoting venous drainage. However, it’s crucial to monitor ICP closely as excessive elevation can sometimes decrease cerebral perfusion pressure. The target is usually a balance guided by neurological assessments.
5. **What are the best practices for preventing patients from sliding down in bed while in semi-Fowler’s position?**
* Use a footboard, employ a draw sheet for repositioning, and consider using a slight knee bend to prevent sliding. Regularly assess and adjust the patient’s position.
6. **Can semi-Fowler’s position be used for patients with feeding tubes? If so, what precautions should be taken?**
* Yes, it’s often used to reduce aspiration risk. Ensure the head of the bed remains elevated during and for at least 30-60 minutes after feeding. Verify proper tube placement and gastric residual volume per facility protocols.
7. **How does semi-Fowler’s position affect blood pressure, and what should I monitor?**
* It can sometimes lower blood pressure, especially in patients with hypovolemia or autonomic dysfunction. Monitor blood pressure regularly, particularly when initially positioning the patient, and watch for signs of dizziness or lightheadedness.
8. **What are the alternative positions to semi-Fowler’s if a patient cannot tolerate it?**
* Alternatives include lateral positioning (side-lying) with head elevation, low-Fowler’s (15-30 degrees), or prone positioning (if appropriate for the patient’s condition and airway management).
9. **How frequently should I reassess a patient’s comfort and skin integrity while they are in semi-Fowler’s position?**
* Reassess comfort and skin integrity at least every 2 hours, or more frequently if the patient is at high risk for skin breakdown or reports discomfort.
10. **What specific documentation is required when placing a patient in semi-Fowler’s position?**
* Document the angle of elevation, the rationale for using the position, any interventions used to prevent skin breakdown (e.g., pressure-redistributing mattress), the patient’s tolerance of the position, and any assessments related to respiratory status or skin integrity.
### Conclusion
In conclusion, semi-Fowler’s position is a fundamental yet powerful technique that significantly contributes to patient comfort, safety, and recovery. By understanding its principles, proper implementation, and potential limitations, healthcare professionals can effectively utilize this position to optimize patient outcomes. Throughout this guide, we’ve emphasized the importance of accurate positioning, pressure ulcer prevention, and continuous monitoring to ensure the best possible care. As leading experts in patient positioning, we advocate for ongoing education and training to further enhance the utilization of semi-Fowler’s position in clinical practice. From our experience, a consistent approach to semi-Fowler’s positioning leads to better patient compliance and improved overall outcomes. Contact our experts for a consultation on implementing semi-Fowler’s position protocols in your healthcare setting.
