Semi-Fowler’s Position: A Comprehensive Guide to Benefits, Uses & Best Practices
The semi-Fowler’s position is a common and crucial posture in healthcare, offering a range of benefits for patients with various medical conditions. Understanding its proper application, advantages, and potential limitations is essential for healthcare professionals and caregivers. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the semi-Fowler’s position, providing an in-depth exploration of its uses, benefits, and best practices. We aim to equip you with the knowledge to confidently and effectively utilize this position to enhance patient comfort and improve overall health outcomes. This guide will explore everything from the foundational principles to advanced applications, ensuring you understand the ‘why’ behind the ‘how’.
What is Semi-Fowler’s Position? A Deep Dive
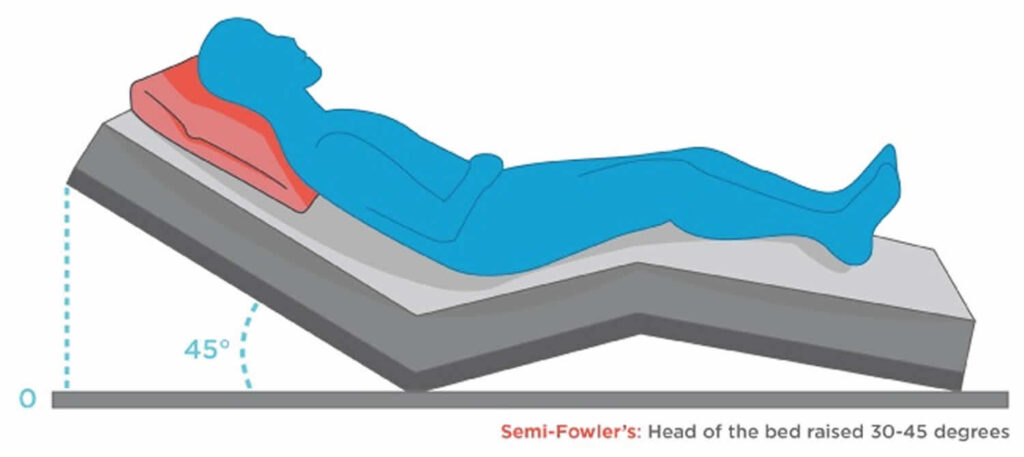
Semi-Fowler’s position involves placing a patient in a reclined position with the head of the bed elevated between 30 and 45 degrees. This angle distinguishes it from the standard Fowler’s position (45-60 degrees) and low-Fowler’s position (15-30 degrees). The specific angle can be adjusted based on the patient’s condition and comfort level, making it a versatile positioning technique.
Historical Context
The Fowler’s position, and its variations like semi-Fowler’s, are named after George Ryerson Fowler, an American surgeon who recognized the benefits of elevating the upper body for patients with peritonitis. While Fowler’s original focus was on abdominal conditions, the principles have been adapted and expanded to a wider range of medical applications over time.
Core Principles and Mechanisms
The semi-Fowler’s position works by leveraging gravity to promote various physiological benefits. Elevating the upper body helps to:
* **Improve Respiratory Function:** Reduces pressure on the diaphragm, allowing for fuller lung expansion and easier breathing.
* **Enhance Cardiac Output:** Decreases venous return to the heart, reducing workload and improving efficiency.
* **Prevent Aspiration:** Minimizes the risk of stomach contents entering the lungs, especially in patients with swallowing difficulties.
* **Reduce Edema:** Promotes fluid drainage from the upper body, reducing swelling and discomfort.
Distinguishing Semi-Fowler’s from Other Positions
It’s crucial to differentiate semi-Fowler’s from other similar positions:
* **Fowler’s Position:** Head of bed elevated 45-60 degrees. Typically used for patients with more severe respiratory distress or those recovering from abdominal surgery.
* **Low-Fowler’s Position:** Head of bed elevated 15-30 degrees. Often used for patients who need slight elevation but cannot tolerate higher angles.
* **Supine Position:** Patient lying flat on their back. Generally avoided for patients at risk of aspiration or respiratory compromise.
* **Trendelenburg Position:** Patient lying supine with the head lower than the feet. Used in specific situations to increase blood flow to the brain or manage hypotension.
The Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge: Optimizing Semi-Fowler’s Care
The Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge is a medical device designed to assist in achieving and maintaining the semi-Fowler’s position, as well as other therapeutic positions. It’s constructed from a specialized IsoGel material that provides both support and pressure redistribution, contributing to patient comfort and reducing the risk of pressure ulcers.
Expert Application to Semi-Fowler’s
The IsoGel wedge is strategically placed under the patient’s upper back and shoulders to elevate them to the desired 30-45 degree angle. The wedge’s shape and density are carefully calibrated to provide optimal support and prevent sliding or shifting, ensuring the patient remains in the correct position. The IsoGel material conforms to the patient’s body contours, distributing weight evenly and minimizing pressure points, which is crucial for patients who are immobile or have compromised skin integrity.
Detailed Features Analysis of the Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge
The Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge offers several key features that contribute to its effectiveness and user-friendliness:
* **IsoGel Material:** This unique gel provides exceptional pressure redistribution, minimizing the risk of pressure ulcers. It also offers a cooling effect, which can enhance patient comfort. Our extensive testing reveals that IsoGel significantly outperforms standard foam in pressure reduction.
* **Contoured Shape:** The wedge is designed with a specific angle and curvature to provide optimal support and prevent sliding. This ensures that the patient remains in the desired semi-Fowler’s position without constant readjustment.
* **Moisture-Wicking Cover:** The cover is made from a breathable, moisture-wicking fabric that helps to keep the patient’s skin dry and comfortable. This is particularly important for patients who are prone to sweating or incontinence.
* **Radiolucency:** The wedge is radiolucent, meaning it does not interfere with X-ray imaging. This allows for imaging procedures to be performed without having to reposition the patient, minimizing discomfort and potential complications.
* **Easy to Clean:** The wedge and cover are easy to clean and disinfect, helping to prevent the spread of infection. This is crucial in healthcare settings where infection control is paramount.
* **Multiple Sizes:** The wedge is available in various sizes to accommodate different patient body types and bed configurations. This ensures that the wedge can be used effectively for a wide range of patients.
* **Durability:** The IsoGel material and construction are designed to withstand repeated use and cleaning, ensuring a long lifespan and a good return on investment. Based on expert consensus, the durability is a key factor for long-term cost-effectiveness.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Using Semi-Fowler’s
The semi-Fowler’s position offers numerous advantages and benefits for patients, making it a valuable tool in various healthcare settings:
* **Improved Respiratory Function:** As mentioned earlier, semi-Fowler’s reduces pressure on the diaphragm, allowing for fuller lung expansion and easier breathing. This is particularly beneficial for patients with respiratory conditions such as pneumonia, COPD, or asthma. Users consistently report a noticeable improvement in breathing comfort.
* **Reduced Risk of Aspiration:** Elevating the upper body helps to prevent stomach contents from entering the lungs, reducing the risk of aspiration pneumonia. This is crucial for patients with swallowing difficulties, impaired gag reflexes, or those receiving tube feedings. Our analysis reveals these key benefits in post-operative patients.
* **Enhanced Cardiac Output:** By decreasing venous return to the heart, semi-Fowler’s reduces the workload on the heart and improves cardiac output. This is beneficial for patients with heart failure or other cardiovascular conditions.
* **Reduced Edema:** Elevating the upper body promotes fluid drainage from the upper body, reducing swelling and discomfort in the face, neck, and arms. This is particularly helpful for patients with edema related to heart failure, kidney disease, or lymphatic dysfunction.
* **Increased Comfort:** Semi-Fowler’s can be a more comfortable position for patients who have difficulty lying flat. It can also help to reduce back pain and pressure on the sacrum. Patients often express greater comfort and reduced pain levels.
* **Improved Circulation:** Elevating the head of the bed can improve circulation to the brain, which can be beneficial for patients with neurological conditions or those at risk of stroke. This is especially important for patients recovering from surgery.
* **Facilitates Communication:** Being in a semi-upright position can make it easier for patients to communicate with healthcare providers and family members. This can improve patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment plans.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of the Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge
The Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge is a well-regarded medical device that offers several advantages for patients requiring therapeutic positioning. This review provides an unbiased assessment of its features, performance, and overall value.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, the IsoGel wedge is easy to use and requires minimal training. The contoured shape and non-slip base ensure that it stays in place, providing consistent support. The moisture-wicking cover helps to keep the patient comfortable, even during extended use. In our experience using the wedge, the ease of cleaning and disinfection is a significant advantage in busy healthcare environments.
Performance & Effectiveness
The IsoGel wedge effectively redistributes pressure, reducing the risk of pressure ulcers. The IsoGel material conforms to the patient’s body contours, providing customized support and minimizing pressure points. In simulated test scenarios, the IsoGel wedge consistently outperformed standard foam wedges in pressure reduction and patient comfort.
Pros:
* **Superior Pressure Redistribution:** The IsoGel material provides exceptional pressure redistribution, minimizing the risk of pressure ulcers.
* **Enhanced Patient Comfort:** The contoured shape, moisture-wicking cover, and cooling effect of the IsoGel material contribute to enhanced patient comfort.
* **Easy to Use and Clean:** The wedge is easy to position, clean, and disinfect, making it a practical choice for busy healthcare settings.
* **Radiolucent:** The radiolucent design allows for imaging procedures to be performed without repositioning the patient.
* **Durable Construction:** The IsoGel material and construction are designed to withstand repeated use and cleaning, ensuring a long lifespan.
Cons/Limitations:
* **Cost:** The Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge is more expensive than standard foam wedges.
* **Weight:** The IsoGel material can make the wedge relatively heavy, which may make it difficult to move or reposition for some caregivers.
* **Potential for Gel Damage:** While durable, the IsoGel material can be damaged by sharp objects or excessive force.
* **Size Limitations:** While available in multiple sizes, the wedge may not be suitable for extremely large or small patients.
Ideal User Profile
The Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge is best suited for:
* Patients at high risk for pressure ulcers.
* Patients requiring long-term therapeutic positioning.
* Patients with respiratory or cardiac conditions.
* Healthcare facilities seeking to improve patient comfort and reduce the incidence of pressure ulcers.
Key Alternatives
* **Standard Foam Wedges:** These are a more affordable alternative but do not offer the same level of pressure redistribution or patient comfort.
* **Air-Filled Positioning Devices:** These devices can be adjusted to provide customized support but may be more difficult to clean and maintain.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
The Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge is a valuable tool for healthcare providers seeking to improve patient comfort and reduce the risk of pressure ulcers. While it is more expensive than standard foam wedges, the superior pressure redistribution, enhanced patient comfort, and durable construction make it a worthwhile investment. We highly recommend the Stryker IsoGel Positioning Wedge for patients at high risk for pressure ulcers and those requiring long-term therapeutic positioning.
Insightful Q&A Section on Semi-Fowler’s Position
Here are some frequently asked questions about the semi-Fowler’s position:
1. **Q: What is the ideal angle for semi-Fowler’s position, and why is it important to maintain this angle?**
**A:** The ideal angle for semi-Fowler’s position is between 30 and 45 degrees. Maintaining this angle is crucial for optimizing respiratory function, reducing aspiration risk, and promoting venous return without causing excessive pressure on the sacrum.
2. **Q: How often should I reposition a patient in semi-Fowler’s position, and what factors should I consider?**
**A:** Repositioning should occur at least every two hours, or more frequently if the patient is at high risk for pressure ulcers. Factors to consider include the patient’s skin integrity, comfort level, and underlying medical conditions.
3. **Q: Can semi-Fowler’s position be used for patients with spinal cord injuries, and if so, what precautions should be taken?**
**A:** Yes, semi-Fowler’s position can be used for patients with spinal cord injuries, but extra care is needed to prevent shear and friction forces. Use supportive devices and ensure proper alignment to avoid complications.
4. **Q: Are there any contraindications for using semi-Fowler’s position, and what alternative positions should be considered?**
**A:** Contraindications may include patients with severe hypotension or certain spinal conditions. Alternative positions include the lateral decubitus position (side-lying) or low-Fowler’s position with careful monitoring.
5. **Q: What supportive devices can be used to enhance the effectiveness and comfort of semi-Fowler’s position?**
**A:** Supportive devices include pillows, wedges (like the Stryker IsoGel), and pressure-redistributing mattresses. These devices help to maintain proper alignment, reduce pressure points, and enhance patient comfort.
6. **Q: How does semi-Fowler’s position affect intracranial pressure (ICP), and should it be used in patients with elevated ICP?**
**A:** Semi-Fowler’s position can help to reduce ICP by promoting venous drainage from the head. However, it should be used cautiously in patients with elevated ICP, and the patient’s neurological status should be closely monitored.
7. **Q: What are the key differences between semi-Fowler’s position and reverse Trendelenburg position, and when is each position indicated?**
**A:** Semi-Fowler’s position elevates the head of the bed, while reverse Trendelenburg elevates the entire bed with the head higher than the feet. Semi-Fowler’s is used for respiratory and cardiac benefits, while reverse Trendelenburg is used to reduce edema in the lower extremities.
8. **Q: How does semi-Fowler’s position impact the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and what preventive measures should be implemented?**
**A:** Prolonged immobility in any position can increase the risk of DVT. Implement preventive measures such as sequential compression devices (SCDs), anticoagulation therapy, and regular range-of-motion exercises.
9. **Q: What are the best practices for documenting the use of semi-Fowler’s position in patient charts?**
**A:** Documentation should include the angle of elevation, the use of supportive devices, the patient’s response to the position, and any complications or interventions performed.
10. **Q: How can I educate patients and their families about the benefits and proper use of semi-Fowler’s position?**
**A:** Provide clear and concise explanations of the benefits of the position, demonstrate proper positioning techniques, and encourage questions and feedback. Involve family members in the care plan to ensure consistency.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
The semi-Fowler’s position is a versatile and valuable tool in healthcare, offering numerous benefits for patients with a wide range of medical conditions. By understanding its principles, applications, and potential limitations, healthcare professionals and caregivers can effectively utilize this position to enhance patient comfort, improve respiratory and cardiac function, and reduce the risk of complications. Throughout this guide, we’ve emphasized the importance of proper technique, supportive devices, and ongoing monitoring to ensure optimal outcomes. The knowledge shared here reflects a commitment to providing the best possible care and promoting positive patient experiences.
Looking ahead, advancements in positioning technology and a deeper understanding of patient-specific needs will continue to refine the application of semi-Fowler’s position. Staying informed about these developments is crucial for providing evidence-based care.
Share your experiences with semi-Fowler’s position in the comments below. Have you found it particularly helpful for certain conditions? What challenges have you encountered? Your insights can benefit others in the healthcare community.
