Decoding Generations: Unveiling the Defining Characteristics
Are you trying to understand why your parents see the world so differently from you? Or perhaps you’re struggling to connect with younger employees who seem to operate on a completely different wavelength? Understanding the *characteristics of different generations* is key to bridging these gaps, fostering better communication, and navigating an increasingly diverse world. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the defining traits of each generation, offering insights you won’t find anywhere else. We’ll explore the historical context, cultural influences, and technological advancements that have shaped each cohort, providing you with the knowledge to effectively interact with and understand individuals from all walks of life. From Baby Boomers to Gen Z, we’ll uncover the nuances that make each generation unique, empowering you to build stronger relationships and create more inclusive environments.
## Understanding Generational Cohorts: A Deep Dive
Generational cohorts are groups of people born within a specific time frame who share similar experiences, values, and beliefs. These shared experiences, often shaped by significant historical events, technological advancements, and cultural trends, contribute to the unique *characteristics of different generations*. While generalizations should be approached with caution, understanding these broad trends can provide valuable insights into how individuals from different generations perceive the world and interact with each other.
### The Significance of Generational Analysis
Analyzing the *characteristics of different generations* isn’t about stereotyping individuals. Instead, it’s about recognizing the potential influence of shared experiences on attitudes, behaviors, and communication styles. This understanding can be invaluable in various contexts, including:
* **Workplace Dynamics:** Fostering collaboration and understanding between employees of different ages.
* **Marketing and Advertising:** Tailoring messaging to resonate with specific generational groups.
* **Education:** Adapting teaching methods to meet the needs of diverse learners.
* **Family Relationships:** Improving communication and empathy between family members.
### Defining Generational Boundaries: A Word of Caution
It’s important to remember that generational boundaries are not rigid. Individuals within a generation can vary widely in their beliefs and behaviors. Furthermore, the exact dates used to define each generation can differ depending on the source. However, the following are generally accepted ranges:
* **The Greatest Generation (born 1901-1927):** Shaped by the Great Depression and World War II, this generation is known for its resilience, patriotism, and strong work ethic.
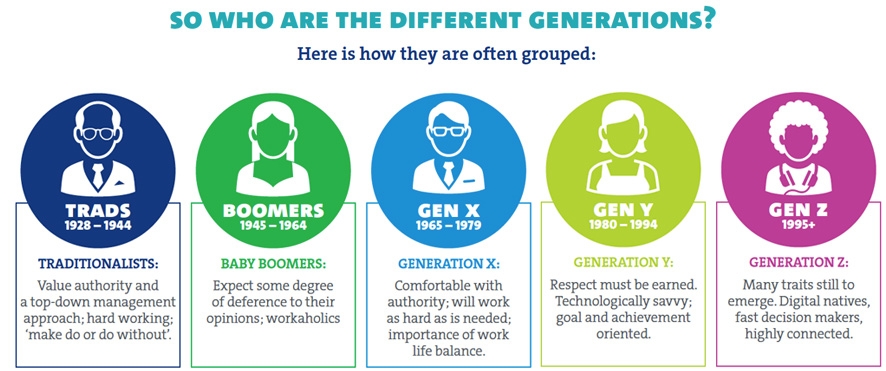
* **The Silent Generation (born 1928-1945):** This generation came of age during a time of conformity and social conservatism. They are often characterized as being hardworking, disciplined, and respectful of authority.
* **Baby Boomers (born 1946-1964):** Born after World War II, this generation experienced a period of economic prosperity and social change. They are often associated with optimism, activism, and a strong sense of individualism.
* **Generation X (born 1965-1980):** This generation came of age during a time of economic uncertainty and rapid technological change. They are often characterized as being independent, resourceful, and skeptical of authority.
* **Millennials (born 1981-1996):** Also known as Generation Y, this generation grew up in the digital age and experienced the rise of the internet and social media. They are often associated with being tech-savvy, collaborative, and socially conscious.
* **Generation Z (born 1997-2012):** This generation has grown up in a world of constant connectivity and instant information. They are often characterized as being digital natives, entrepreneurial, and adaptable.
* **Generation Alpha (born 2013-2025):** The children of Millennials, this generation is growing up in an even more technologically advanced world. Their *characteristics* are still evolving, but they are expected to be highly connected, globally aware, and innovative.
## Understanding Each Generation: Key Characteristics
Let’s take a closer look at the defining *characteristics of different generations*, exploring their values, beliefs, and experiences in more detail.
### The Greatest Generation: Resilience and Patriotism
* **Defining Events:** The Great Depression and World War II.
* **Core Values:** Duty, honor, hard work, frugality, and patriotism.
* **Communication Style:** Respectful, formal, and direct.
* **Work Ethic:** Strong work ethic, loyalty, and dedication.
This generation experienced immense hardship during the Great Depression and then went on to fight in World War II. These experiences instilled in them a deep sense of resilience, duty, and patriotism. They are known for their strong work ethic, their commitment to their communities, and their respect for authority.
### The Silent Generation: Conformity and Discipline
* **Defining Events:** Post-World War II era, the Korean War, and the rise of suburbia.
* **Core Values:** Conformity, stability, discipline, and respect for authority.
* **Communication Style:** Reserved, polite, and formal.
* **Work Ethic:** Hardworking, loyal, and dedicated to their employers.
The Silent Generation came of age during a time of social conservatism and conformity. They are known for their hard work, their discipline, and their respect for authority. They tend to be fiscally conservative and value stability and security.
### Baby Boomers: Optimism and Individualism
* **Defining Events:** The Vietnam War, the Civil Rights Movement, and the rise of the counterculture.
* **Core Values:** Optimism, individualism, social justice, and personal growth.
* **Communication Style:** Assertive, expressive, and collaborative.
* **Work Ethic:** Driven, competitive, and results-oriented.
Baby Boomers experienced a period of economic prosperity and social change. They are known for their optimism, their individualism, and their desire to make a difference in the world. They are often associated with the counterculture movement and the fight for civil rights.
### Generation X: Independence and Resourcefulness
* **Defining Events:** The rise of personal computers, the AIDS epidemic, and economic recessions.
* **Core Values:** Independence, resourcefulness, skepticism, and work-life balance.
* **Communication Style:** Direct, informal, and pragmatic.
* **Work Ethic:** Independent, self-reliant, and focused on results.
Generation X came of age during a time of economic uncertainty and rapid technological change. They are known for their independence, their resourcefulness, and their skepticism of authority. They value work-life balance and are often entrepreneurial in spirit. “Latchkey kids” is a common term associated with this generation, due to the increased number of working parents.
### Millennials: Tech-Savvy and Socially Conscious
* **Defining Events:** The rise of the internet and social media, the 9/11 terrorist attacks, and the Great Recession.
* **Core Values:** Collaboration, social justice, technology, and work-life integration.
* **Communication Style:** Digital, informal, and collaborative.
* **Work Ethic:** Collaborative, adaptable, and purpose-driven.
Millennials grew up in the digital age and experienced the rise of the internet and social media. They are known for their tech-savviness, their collaborative spirit, and their desire to make a positive impact on the world. They value work-life integration and are often drawn to companies with strong social missions.
### Generation Z: Digital Natives and Adaptable
* **Defining Events:** Constant connectivity, social media, climate change, and global pandemics.
* **Core Values:** Authenticity, diversity, practicality, and financial security.
* **Communication Style:** Visual, digital, and direct.
* **Work Ethic:** Entrepreneurial, adaptable, and focused on skills development.
Generation Z has grown up in a world of constant connectivity and instant information. They are known for being digital natives, their entrepreneurial spirit, and their adaptability. They are highly aware of social and environmental issues and are often driven by a desire to make a difference in the world. They are also more financially conservative than previous generations, having witnessed the impact of economic downturns.
### Generation Alpha: The Future is Now
* **Defining Events:** The rise of artificial intelligence, personalized technology, and a rapidly changing world.
* **Core Values:** Still evolving, but likely to be shaped by technology, globalization, and social responsibility.
* **Communication Style:** Expected to be highly visual, digital, and personalized.
* **Work Ethic:** Likely to be adaptable, innovative, and focused on lifelong learning.
Generation Alpha is the youngest generation and is still developing its *characteristics*. However, it is clear that they will be shaped by technology, globalization, and a rapidly changing world. They are expected to be highly connected, globally aware, and innovative.
## Generational Differences in the Workplace
Understanding the *characteristics of different generations* is particularly important in the workplace. Generational differences can impact communication styles, work ethics, and expectations, leading to misunderstandings and conflict. By recognizing and appreciating these differences, organizations can create more inclusive and productive work environments.
### Communication Styles
* **Baby Boomers:** Prefer face-to-face communication and formal meetings.
* **Generation X:** Value direct and efficient communication, often using email and instant messaging.
* **Millennials:** Rely heavily on digital communication, including social media and collaboration tools.
* **Generation Z:** Prefer visual communication, such as videos and images, and are comfortable with a wide range of digital platforms.
### Work Ethic and Values
* **Baby Boomers:** Value hard work, loyalty, and dedication to their employers.
* **Generation X:** Prioritize work-life balance and are often entrepreneurial in spirit.
* **Millennials:** Seek purpose and meaning in their work and value collaboration and social impact.
* **Generation Z:** Are focused on skills development and are adaptable to changing work environments.
### Managing Generational Differences
To effectively manage generational differences in the workplace, organizations should:
* **Promote open communication:** Encourage employees to share their perspectives and experiences.
* **Provide training on generational differences:** Help employees understand the values, beliefs, and communication styles of different generations.
* **Create inclusive policies and practices:** Ensure that all employees feel valued and respected.
* **Foster mentorship programs:** Pair older and younger employees to share knowledge and skills.
## Bridging the Generational Gap: Practical Strategies
Beyond the workplace, understanding the *characteristics of different generations* can help bridge the gap in various aspects of life. Here are some practical strategies:
* **Active Listening:** Truly listen to understand the perspectives of those from different generations, rather than simply waiting to speak.
* **Empathy and Understanding:** Try to put yourself in their shoes and understand the experiences that have shaped their views.
* **Respect for Differences:** Acknowledge and respect the differences in values, beliefs, and communication styles.
* **Open-Mindedness:** Be open to learning from others, regardless of their age or background.
* **Finding Common Ground:** Focus on shared interests and goals to build connections.
## Generational Marketing: Tailoring Your Message
In the world of marketing, understanding generational *characteristics* is paramount. Different generations respond to different messaging, platforms, and approaches. Tailoring your marketing strategy to resonate with specific generational groups can significantly improve your results.
### Key Considerations for Generational Marketing
* **Platform Preferences:** Where does your target generation spend their time online? (e.g., Facebook for Boomers, TikTok for Gen Z).
* **Messaging:** What kind of language and tone resonates with them? (e.g., practical and informative for Gen X, authentic and purpose-driven for Millennials).
* **Values:** What values are important to them? (e.g., security for Boomers, social impact for Gen Z).
* **Visuals:** What kind of images and videos appeal to them? (e.g., nostalgic imagery for Boomers, trendy and visually appealing content for Gen Z).
### Examples of Generational Marketing Strategies
* **Targeting Baby Boomers:** Focus on value, quality, and reliability. Use traditional marketing channels like print and television. Highlight the benefits of your product or service for their health and well-being.
* **Targeting Generation X:** Emphasize practicality, convenience, and value for money. Use a mix of online and offline marketing channels. Highlight the time-saving benefits of your product or service.
* **Targeting Millennials:** Focus on authenticity, social impact, and experiences. Use social media marketing, influencer marketing, and content marketing. Highlight the positive impact of your product or service on the world.
* **Targeting Generation Z:** Emphasize visual content, authenticity, and social responsibility. Use TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube marketing. Highlight the trendy and innovative aspects of your product or service.
## The Future of Generations: Evolving Trends
The *characteristics of different generations* are constantly evolving, shaped by ongoing technological advancements, social changes, and global events. It’s important to stay informed about these trends to better understand the future of generations.
### Key Trends to Watch
* **Increased Technological Integration:** Future generations will be even more deeply integrated with technology, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.
* **Greater Globalization:** Increased interconnectedness will lead to a more diverse and globally aware population.
* **Focus on Sustainability:** Environmental concerns will continue to shape the values and behaviors of future generations.
* **Emphasis on Personalized Experiences:** Individuals will increasingly expect personalized products, services, and experiences.
* **Lifelong Learning:** The rapid pace of change will require individuals to continually learn and adapt throughout their lives.
## Expert Q&A on Generational Characteristics
Here are some frequently asked questions about the *characteristics of different generations*, answered by experts in the field:
**Q1: Is it fair to generalize about entire generations?**
A: While generalizations can be helpful for understanding broad trends, it’s crucial to remember that individuals within a generation vary widely. Generational analysis should be used as a starting point for understanding, not as a basis for stereotyping.
**Q2: How much does socioeconomic status influence generational characteristics?**
A: Socioeconomic status plays a significant role. Shared economic experiences within a generation can shape attitudes towards work, money, and opportunity. However, this influence interacts with other factors like race, ethnicity, and geographic location.
**Q3: Are there significant differences between generations in different countries?**
A: Yes, cultural context significantly influences generational *characteristics*. While some global trends exist, the specific experiences and values of each generation can vary greatly depending on the country and culture.
**Q4: How are the characteristics of Generation Alpha expected to differ from those of Generation Z?**
A: Generation Alpha is expected to be even more digitally native, accustomed to personalized technology, and potentially more focused on sustainability and social impact. They will also likely be more globally connected from a younger age.
**Q5: What are the biggest challenges facing employers when managing a multigenerational workforce?**
A: Common challenges include communication differences, conflicting work styles, varying expectations for work-life balance, and difficulty attracting and retaining employees from different generations.
**Q6: How can parents better understand their children from different generations?**
A: Open communication, active listening, and a willingness to understand their children’s perspectives are key. Parents should also try to learn about the cultural and technological influences that have shaped their children’s generation.
**Q7: What is the role of education in shaping generational characteristics?**
A: Education plays a crucial role in shaping values, skills, and knowledge. Educational systems can influence how generations perceive the world and prepare them for the challenges and opportunities they will face.
**Q8: How can marketers effectively target multiple generations with a single campaign?**
A: Focus on universal values and themes that resonate across generations. Use a mix of marketing channels and tailor your messaging to appeal to different segments within each generation. Emphasize the benefits of your product or service for each group.
**Q9: What are some common misconceptions about different generations?**
A: Common misconceptions include stereotyping Baby Boomers as resistant to change, Generation X as cynical and apathetic, Millennials as entitled and lazy, and Generation Z as addicted to technology. These stereotypes are often inaccurate and can lead to misunderstandings.
**Q10: How can individuals bridge the generational gap in their personal lives?**
A: Show genuine curiosity about others’ experiences, actively listen to their perspectives, and find common ground based on shared interests and values. Avoid making assumptions or judgments based on age.
## Conclusion: Embracing Generational Diversity
Understanding the *characteristics of different generations* is essential for navigating an increasingly complex and diverse world. By recognizing the unique experiences, values, and beliefs of each generation, we can foster better communication, build stronger relationships, and create more inclusive environments. While generalizations should be approached with caution, understanding these broad trends can provide valuable insights into how individuals from different generations perceive the world and interact with each other. As the world continues to evolve, it’s crucial to stay informed about the changing *characteristics* of generations to effectively connect with and understand those around us.
Now, we encourage you to share your own experiences and insights on generational dynamics in the comments below. How have you seen generational differences impact your workplace, family, or community? Your contributions can help us all learn and grow together.
